本文参考链接:https://msestudent.com/interstitial-sites-size-types-applications-and-calculations/
| Crystal Structure | BCC | FCC | HCP | SC |
| Octahedral Interstitial Site Radius | 0.155r | 0.414r | 0.414r | – |
| Tetrahedral Interstitial Site Radius | 0.291r | 0.225r | 0.225r | – |
| Cubic Interstitial Site Radius | – | – | – | 0.732r |
| Fraction of a cell’s volume occupied by interstitial sites | 10.81% | 6.94% | 6.94% | 20.54% |
- Basic of Interstitial Sites
- 对角线标定法
Basic of Interstitial Sites
Interstitial sites are empty spaces in a crystal lattice.
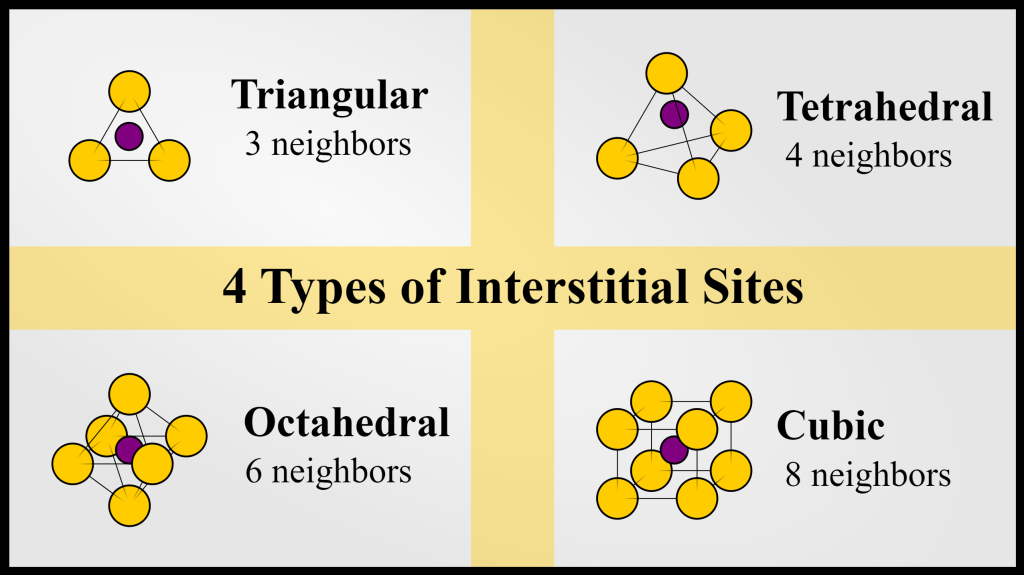
Depending on the number of atoms surrounding that empty space, the interstitial site can be designated as triangular (3), tetrahedral (4), octahedral (6), or cubic (8).
在一个 perfect crystal 中,每个 interstitial site 都是空的,但是由于这些是晶体中空隙最多的区域,imperfect crystals 中偶尔会有原子占据这些位点.
When the interstitial site is not empty, it is considered an “interstitial defect.” Defects allow some of the most important material properties, such as ductility in metals.
4 Types of Interstitial Sites
- triangular
- tetrahedral
- octahedral
- cubic
triangular interstitial site
A triangular interstitial site has 3 surrounding atoms.
All 3 atoms, and the interstitial site, are in the same plane.
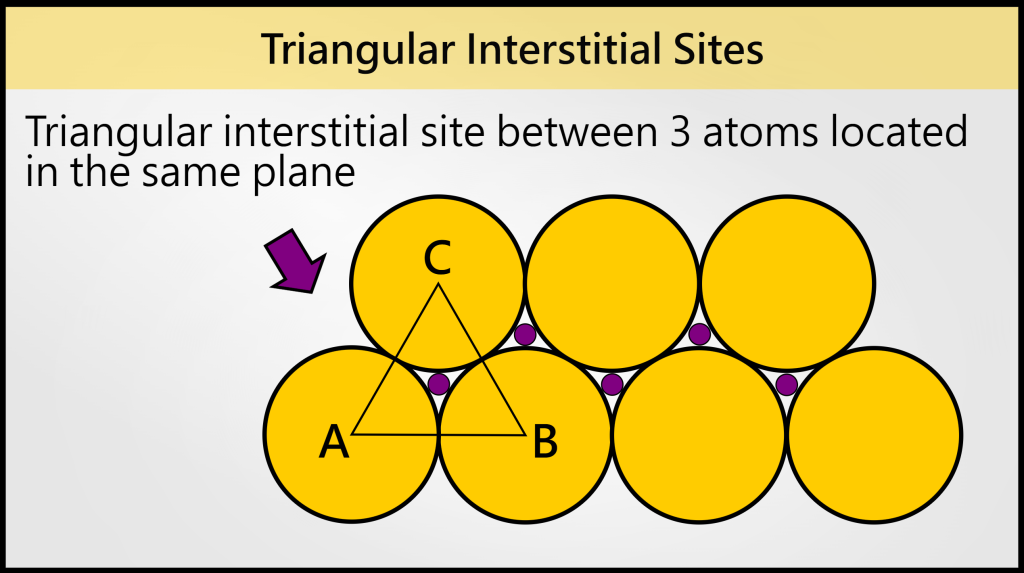
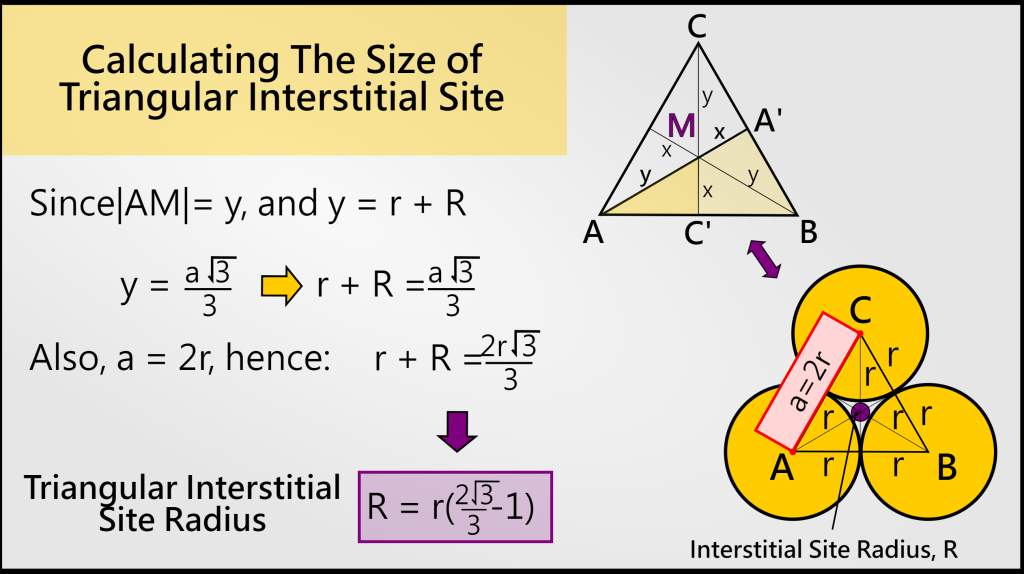
3个包围原子和间隙位本身都位于一个 2D plane 内,没有三维偏移(no out-of-plane deviation);这不同于其他间隙位,如 tetrahedral 或 octahedral,那些是 3D 当中的间隙类型;换言之,如果原子不在同一平面,间隙位会变形或成为其他类型.
tetrahedral interstitial site
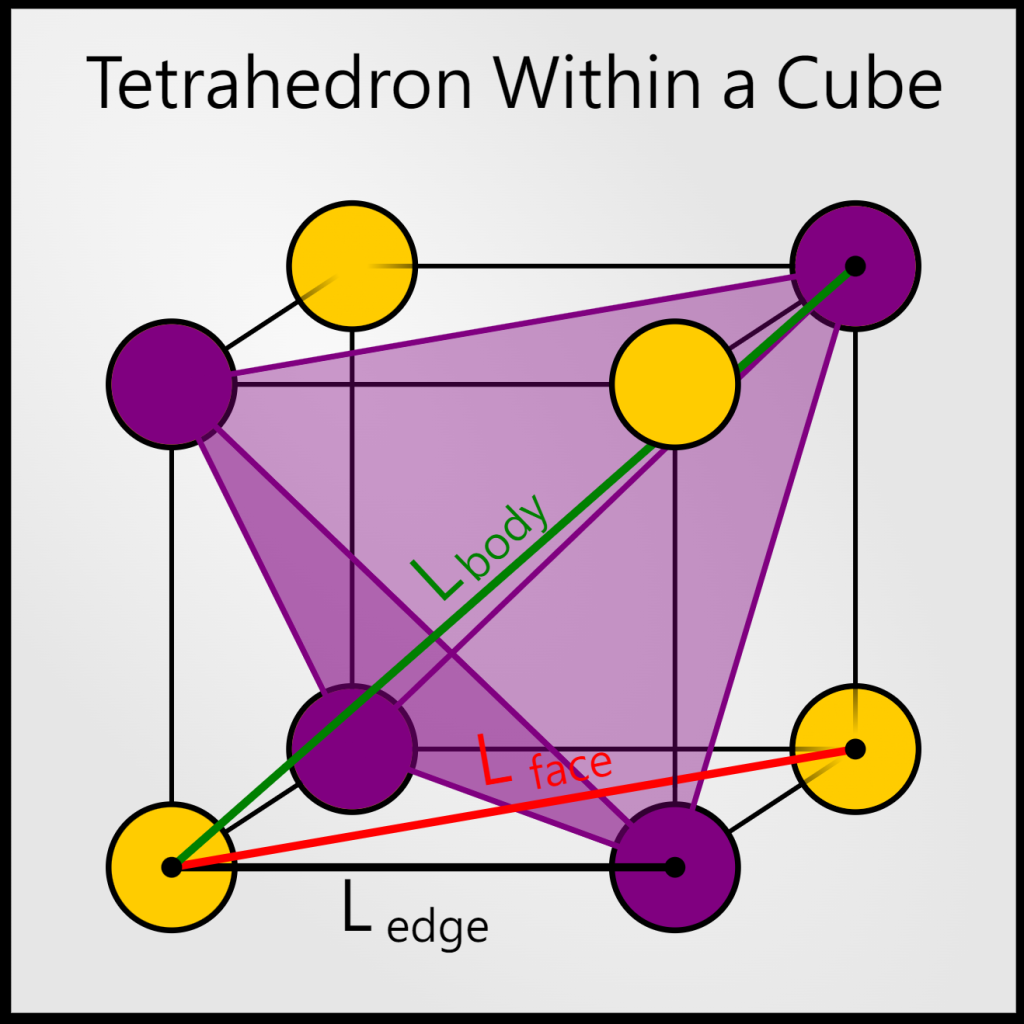
Interstitial Sites in FCC
octahedral interstitial sites
FCC 共有4个octahedral interstitial sites.
unit cell 的边界属于 imaginary boundaries,实际晶体中,相邻单元胞 seamlessly connected;边中点的八面体位正好在两条边交界处,被4个单元胞共享(因为边是四个面相交的线).
所以,计算总数量时:中心1个(完全属于这个单元胞) + 12个边中点(每个贡献1/4,所以12×1/4=3) = 总共 4 个 octahedral interstitial sites.
FCC是 highly symmetric,所以可以用 projection 简化.
tetrahedral interstitial sites
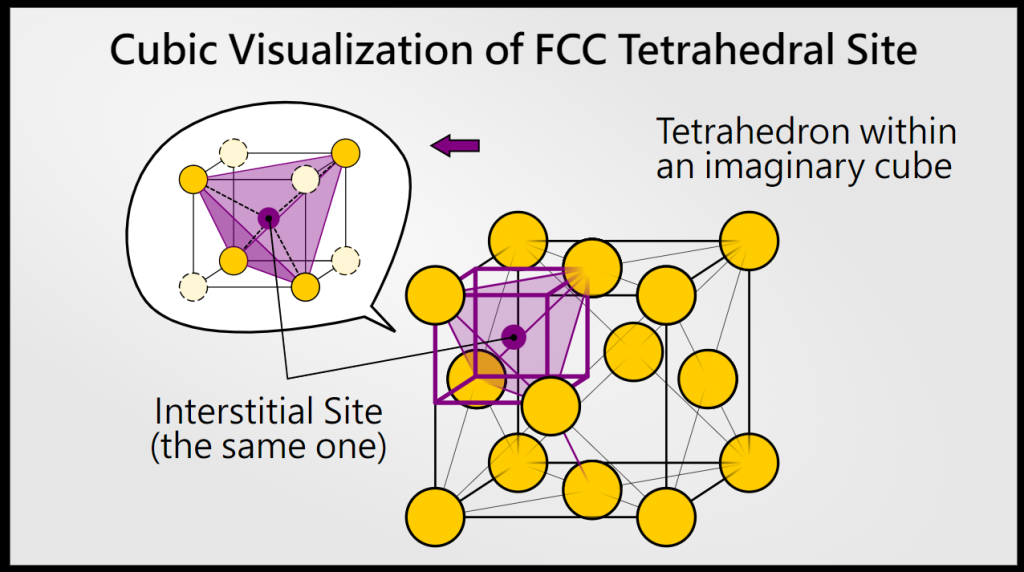
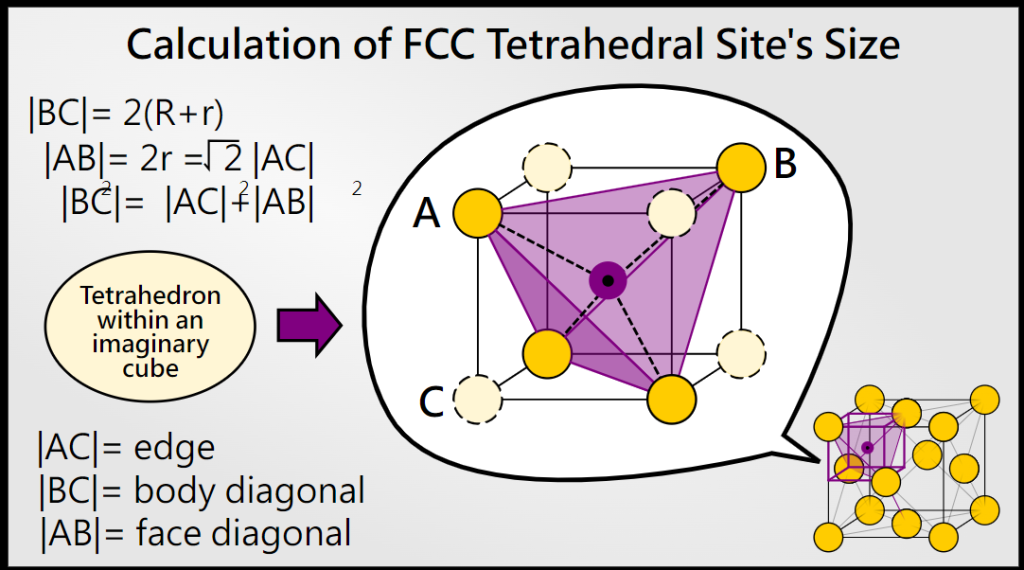
在FCC单元胞中,有8个 tetrahedral interstitial sites.
四面体位由4个原子包围,形成 regular tetrahedron;在FCC中,这些位点位于单元胞的每个 corner 附近;具体来说,每个 orner atom 上方或下方有一个四面体位,但由于对称性,每个单元胞的8个角各贡献一个位点.
Interstitial Sites in BCC
The BCC crystal has 12 tetrahedral sites and 6 octahedral sites.
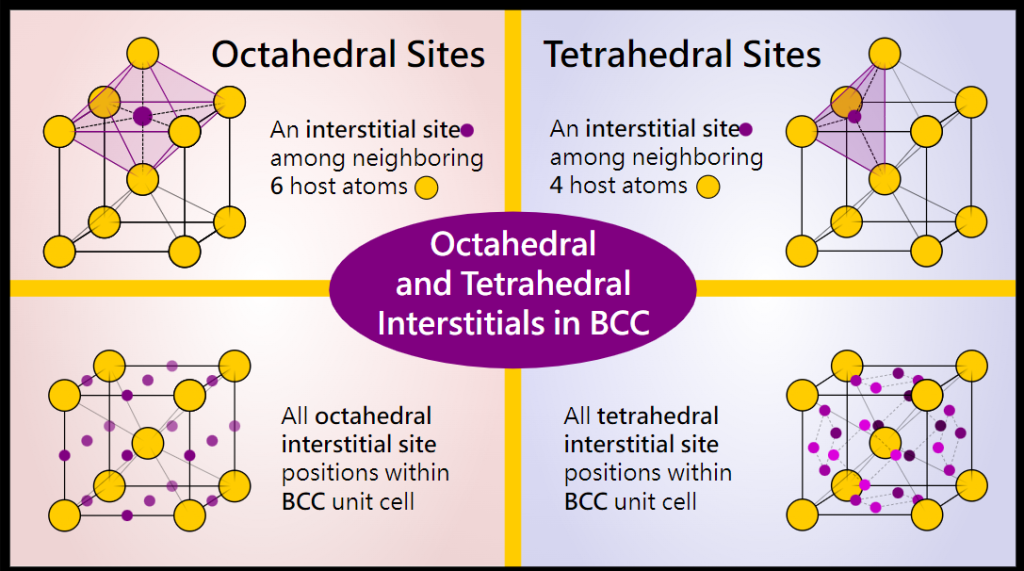
octahedral interstitial sites
BCC单元胞中有6个 octahedral interstitial sites,位点分布在:
- edge centers
- 每个立方体 edge 的中点有一个八面体位;BCC有12条边,所以12个这样的位点
- 每个 edge 的中点被4个单元胞共享;所以,贡献 = 12 × (1/4) = 3
- face centers
- 每个立方体 face 的中心有一个八面体位;BCC有6个面,所以6个这样的位点
- 每个面中心被2个单元胞共享(shared by 2 unit cells,因为面是两个单元胞的界面);所以,贡献 = 6 × (1/2) = 3
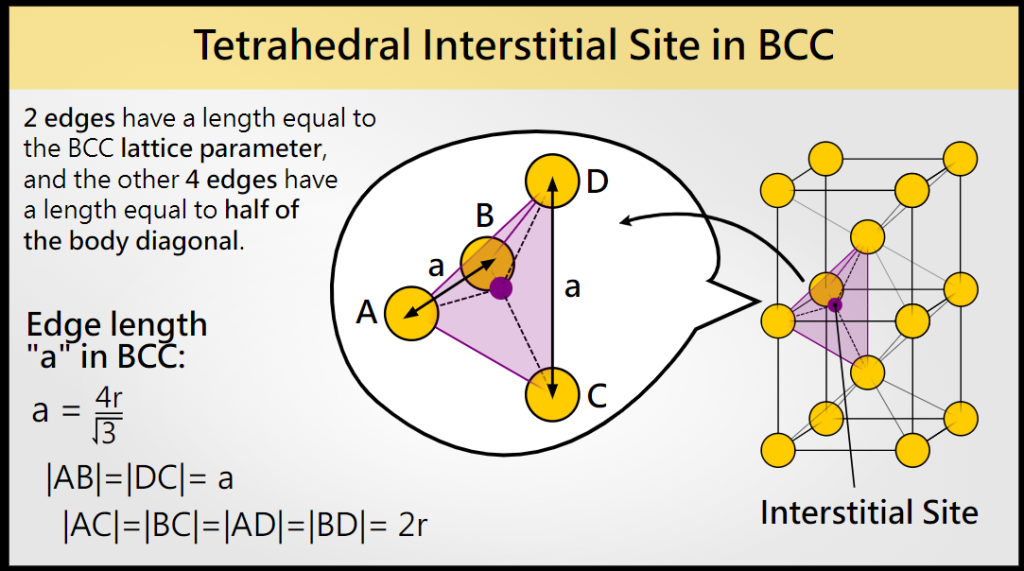
tetrahedral interstitial sites
BCC单元胞中有12个 tetrahedral interstitial sites;这些位点全部分布在立方体的6个 faces 上,没有边中点或体中心的独立位点;每个面有4个四面体位,位于面的 quadrant positions.
详细位置描述:
每个面上的分布: 想象一个 square face ,它由4个 corner atoms 包围,中心无原子;四面体位不是在面中心,而是偏离中点,位于面的四个 quarter positions;BCC有6个面,每个面4个位点,所以总24个 raw positions:
面位点: 每个四面体位位于 face 上,被2个单元胞共享(因为 face 是两个相邻单元胞的界面);所以,贡献 = 总24个位点 × (1/2) = 12.
总和: 就是12个四面体位,没有其他贡献(如 edge 或 corner),因为BCC的 ymmetry 将所有四面体位限制在面上.
注意: BCC没有“体内部”(body interior)的四面体位,因为体心原子占据了中心空间;这些位点“贴近”面,但几何上由体心原子参与包围.
为什么每个面正好4个?这是BCC的点群对称(point group symmetry)决定的——每个面像一个“十字”分布(cross-like),确保均匀.
Interstitial Sites in HCP
Interstitial Sites in Simple Cubic
Interstitial Carbon in Steel
对角线标定法
FCC的间隙
FCC 的间隙完全可以通过 “正方体晶胞的 3 种对角线” 定位,之前算过 FCC 晶胞原子数 = 4(8×1/8 + 6×1/2=4),现在详细讲间隙的 “对角线定位”:
1. Tetrahedral Interstices:用 Body Diagonal 定位
- 定位方法:每条体对角线上有2 个四面体间隙,且这 2 个间隙完全在晶胞内(不与其他晶胞共用,贡献比例 = 1)
- 间隙数计算:4 条体对角线 × 2 个 / 条 = 8 个四面体间隙 → 8=2×4(4 是 FCC 原子数),符合 “四面体间隙 = 2× 密堆积原子数”
为什么在体对角线?因为四面体间隙需要 4 个原子围成,体对角线中点附近的间隙,正好被 “1 个顶点原子 + 3 个相邻面心原子” 包围,形成四面体结构.
2. Octahedral Interstices:用 Body Diagonal + Edge Midpoint 定位
八面体间隙分两类,位置不同,需分别用两种对角线辅助判断:
- 第一类: Body Center → 用体对角线定位体心位置的间隙,被 “6 个面心原子” 包围(前后左右上下各 1 个面心),形成正八面体结构,这个间隙完全在晶胞内,贡献 = 1
- 第二类:Edge Midpoint → 用棱边对角线定位正方体有 12 条棱,每条棱的中点有 1 个间隙,这个间隙被 “4 个晶胞共用”(比如前面一条棱的中点,属于当前晶胞和右侧、上方、前方的 3 个相邻晶胞),贡献比例 = 1/4
- 间隙数计算:体心 1 个 +(12 条棱 ×1/4)= 1+3=4 个八面体间隙 → 4=1×4(FCC 原子数),符合 “八面体间隙 = 1× 密堆积原子数”
为什么用棱边对角线?棱边中点的间隙,正好被 “2 个顶点原子 + 2 个相邻面心原子” 包围,加上对面棱边的原子,形成八面体结构
BCC:用 Body Diagonal + Face Diagonal 定位
BCC 不是最密堆积,间隙比 FCC 少,先算 BCC 晶胞原子数:顶点 8 个 ×1/8 + 体心 1 个 ×1=2 个(原子数 = 2)
1. Tetrahedral Interstices:用 Body Diagonal 定位
- 定位方法:BCC 的体对角线长是 “棱长的√3 倍”,在体对角线上,距离顶点 1/4 和 3/4 处各有 1 个四面体间隙(1 条体对角线有 2 个间隙)。这些间隙被 “2 个顶点原子 + 2 个体心附近的原子” 包围,形成四面体结构
- 间隙数计算:4 条体对角线 × 2 个 / 条 = 8 个四面体间隙 → 比例:8=4×2(BCC 原子数 = 2),注意:BCC 的四面体间隙比例是 4 倍,不是 FCC 的 2 倍(因为 BCC 不是最密堆积)
2. Octahedral Interstices:用 Body Diagonal + Edge Midpoint 定位
- 定位方法分两类:
- face diagonal midpoint:正方体 6 个面,每个面的面对角线中点有 1 个间隙,被 “4 个顶点原子” 包围,贡献比例 = 1/2(1 个面对角线中点属于 2 个晶胞)
- 棱边中点:12 条棱,每条棱边中点有 1 个间隙,贡献比例 = 1/4(和 FCC 类似)
- 间隙数计算:(6 个面 ×1/2) +(12 条棱 ×1/4)= 3+3=6 个八面体间隙 → 比例:6=3×2(BCC 原子数 = 2)
3. HCP:用 Height of Hexagonal Prism + Face diagonal of the bottom 定位
HCP 的晶胞是 “六方柱”(上下两个正六边形底面,中间一个矩形侧面),原子数 = 6(顶点 12 个 ×1/6 + 底面中心 2 个 ×1/2 + 中间层 3 个 ×1=6)
1. Tetrahedral Interstices:用 Height of Hexagonal Prism 定位
- 定位方法:六方柱的轴向(上下底面中心的连线)附近,有 2 组四面体间隙,每组 6 个,共 12 个。每个间隙被 “4 个原子” 包围(2 个底面原子 + 2 个中间层原子),通过轴向可以快速找到间隙的分层位置。
- 间隙数计算:12 个 → 12=2×6(HCP 原子数 = 6),符合 “四面体间隙 = 2× 密堆积原子数”。
2. Octahedral Interstices:用 Face diagonal of the bottom + Height of Hexagonal Prism 定位
- 定位方法:分两类:① 上下底面之间的 “中间层”:3 个八面体间隙,完全在晶胞内;② 上下底面的 “边缘附近”:3 个八面体间隙,与相邻晶胞共用,贡献比例 = 1/2
- 间隙数计算:3 + 3=6 个 → 6=1×6(HCP 原子数 = 6),符合 “八面体间隙 = 1× 密堆积原子数”
14 种布拉维晶格的间隙数总结
不用记全 14 种,只记以下 3 种核心晶格,用表格整理更清晰:
| Bravais Lattice Type | Number of Atoms per Unit Cell | Number of Tetrahedral Interstices | Number of Octahedral Interstices | Interstice Location Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCC | 4 | 8(2×4) | 4(1×4) | 四面体:体对角线;八面体:体心 + 棱边对角线 |
| BCC | 2 | 8(4×2) | 6(3×2) | 四面体:体对角线;八面体:面对角线 + 棱边中点 |
| HCP | 6 | 12(2×6) | 6(1×6) | 四面体:六方柱轴向;八面体:中间层 + 底面边缘 |
0 条评论