Laplace Transform 是解决线性微分方程 Linear Ordinary Differential Equation, ODE 和 Partial Differential Equation, PDE 的核心工具,能将复杂的微积分运算转化为简单的代数运算,在材料科学、化工、电子等领域广泛应用.
I Key Concepts
1. Purpose
- 将 time domain 的函数 \(f(t)\) 转化为 frequency domain 的函数 \(F(s)\),把微分方程 differential equation 转化为 algebraic equation,简化求解
2. Definition
拉普拉斯变换的数学定义为:
$$\mathcal{L}\{f(t)\} = F(s) = \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-st} f(t) dt$$
- 关键符号说明:
- \(\mathcal{L}\):拉普拉斯变换算子(Laplace transform operator)
- \(f(t)\):时域函数(time domain function),小写字母表示
- \(F(s)\):拉普拉斯变换结果(Laplace transform),对应大写字母表示
- \(s = \sigma + i\omega\):复变量(complex variable),\(\sigma\) 为实部(real part,与指数衰减 / 增长相关),\(\omega\) 为角频率(angular frequency,单位 rad/s,与振荡相关)
- \(e^{-st} = e^{-\sigma t} e^{-i\omega t}\):核函数(kernel function),\(e^{-\sigma t}\) 是指数衰减项(exponential decay term),\(e^{-i\omega t} = \cos\omega t + i\sin\omega t\)(欧拉公式,Euler’s formula)是振荡项(oscillation term)
二、Basic Laplace Transform Calculations
1. Common Functions
(1)Constant Function:\(f(t) = 1\)(\(t \geq 0\))
\(\mathcal{L}\{1\} = \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-st} dt = \frac{1}{s} \quad (s > 0, \text{收敛条件convergence condition})\)
(2)Exponential Function:\(f(t) = e^{at}\)(\(a > 0\))
\(\mathcal{L}\{e^{at}\} = \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-(s-a)t} dt = \frac{1}{s – a} \quad (s > a, \text{收敛条件})\)
- 推论:\(f(t) = e^{-at}\) 时,\(\mathcal{L}\{e^{-at}\} = \frac{1}{s + a} \quad (s > -a)\)
(3)Power Function:\(f(t) = t^n\)(n 为非负整数)
\(\mathcal{L}\{t^n\} = \frac{n!}{s^{n+1}} \quad (s > 0)\)
- 特例:\(n=1\) 时,\(\mathcal{L}\{t\} = \frac{1}{s^2}\);\(n=4\) 时,\(\mathcal{L}\{t^4\} = \frac{24}{s^5}\)
(4)Trigonometric Functions
\(\mathcal{L}\{\sin\omega t\} = \frac{\omega}{s^2 + \omega^2}, \quad \mathcal{L}\{\cos\omega t\} = \frac{s}{s^2 + \omega^2} \quad (s > 0)\)
(5)Hyperbolic Functions
\(\mathcal{L}\{\sinh\omega t\} = \frac{\omega}{s^2 – \omega^2}, \quad \mathcal{L}\{\cosh\omega t\} = \frac{s}{s^2 – \omega^2} \quad (s > |\omega|)\)
(6)Heaviside Function/Unit Step Function:\(u(t – a)\)
定义:\(u(t – a) = \begin{cases} 0, & t < a \\ 1, & t \geq a \end{cases}\)(\(a \geq 0\))
\(\mathcal{L}\{u(t – a)\} = \frac{e^{-as}}{s} \quad (s > 0)\)
- 特例:\(a=0\) 时,\(u(t)\) 为单位阶跃函数,\(\mathcal{L}\{u(t)\} = \frac{1}{s}\)
2. Key Properties
(1)Linearity
对常数 \(a, b\),有:
\(\mathcal{L}\{af(t) + bg(t)\} = a\mathcal{L}\{f(t)\} + b\mathcal{L}\{g(t)\}\)
\(\mathcal{L}^{-1}\{aF(s) + bG(s)\} = a\mathcal{L}^{-1}\{F(s)\} + b\mathcal{L}^{-1}\{G(s)\}\)
- 应用:拆分复杂函数为基本函数的线性组合,分别求变换。
(2)Shift Theorem
- 时域平移(Time Shift):\(\mathcal{L}\{f(t – a)u(t – a)\} = e^{-as}F(s)\)(\(a \geq 0\))
- 频域平移(Frequency Shift):\(\mathcal{L}\{e^{-at}f(t)\} = F(s + a)\)
- 推论:\(\mathcal{L}\{e^{at}f(t)\} = F(s – a)\)
- 应用:处理含指数函数与其他函数乘积的情况,如 \(\mathcal{L}\{e^{-at}\cos\omega t\} = \frac{s + a}{(s + a)^2 + \omega^2}\)
三、Inverse Laplace Transform
1. Definition
若 \(\mathcal{L}\{f(t)\} = F(s)\),则逆变换为:
\(\mathcal{L}^{-1}\{F(s)\} = f(t)\)
- 核心方法:查表法(Table Lookup)+ 部分分式分解(Partial Fractions)
2. Partial Fractions
(1)适用场景
当 \(F(s) = \frac{N(s)}{D(s)}\)(有理函数),且 \(\deg(N(s)) < \deg(D(s))\) 时,分解为简单分式:
- distinct linear factors( distinct linear factors):\(\frac{N(s)}{(s – a)(s – b)} = \frac{A}{s – a} + \frac{B}{s – b}\)
- 重复线性因式(Repeated Linear Factors):\(\frac{N(s)}{(s – a)^2} = \frac{A}{s – a} + \frac{B}{(s – a)^2}\)
- 不可约二次因式(Irreducible Quadratic Factors):\(\frac{N(s)}{(s^2 + \omega^2)(s – a)} = \frac{As + B}{s^2 + \omega^2} + \frac{C}{s – a}\)
(2)示例
求 \(\mathcal{L}^{-1}\left\{\frac{s^2 + s + 1}{s(s^2 + 1)}\right\}\):
- 分解:\(\frac{s^2 + s + 1}{s(s^2 + 1)} = \frac{1}{s} + \frac{1}{s^2 + 1}\)
- 查表逆变换:\(\mathcal{L}^{-1}\left\{\frac{1}{s}\right\} = 1\),\(\mathcal{L}^{-1}\left\{\frac{1}{s^2 + 1}\right\} = \sin t\)
- 结果:\(1 + \sin t\)
四、Transforming Derivatives
1. Core Formulas
设 \(\mathcal{L}\{f(t)\} = F(s)\),则:
- First Derivative:\(\mathcal{L}\left\{\frac{df}{dt}\right\} = sF(s) – f(0)\)
- Second Derivative:\(\mathcal{L}\left\{\frac{d^2f}{dt^2}\right\} = s^2F(s) – sf(0) – f'(0)\)
- Third Derivative:\(\mathcal{L}\left\{\frac{d^3f}{dt^3}\right\} = s^3F(s) – s^2f(0) – sf'(0) – f”(0)\)
- 关键:自动包含 initial conditions,无需单独求解 homogeneous solution 和 particular solution
2. 验证示例(Verification Example)
若 \(f(t) = \sin t\),则 \(f(0) = 0\),\(\mathcal{L}\{\sin t\} = \frac{1}{s^2 + 1}\):
\(\mathcal{L}\left\{\frac{df}{dt}\right\} = s \cdot \frac{1}{s^2 + 1} – 0 = \frac{s}{s^2 + 1} = \mathcal{L}\{\cos t\}\)
- 符合预期,验证公式正确性。
五、用拉普拉斯变换解 ODE(Solving ODEs Using Laplace Transforms)
1. 三步法(Three-Step Method)
- 对 ODE 两边取拉普拉斯变换(Take Laplace Transform on Both Sides),转化为代数方程;
- 代入初始条件(Substitute Initial Conditions),解出 \(F(s)\);
- 对 \(F(s)\) 取逆拉普拉斯变换(Take Inverse Laplace Transform),得到 \(f(t)\)。
2. 一阶 ODE 示例(First-Order ODE Example)
求解:\(\frac{dx}{dt} = 3x + 6\),\(x(0) = 2\)
- 变换:\(sX(s) – x(0) = 3X(s) + \frac{6}{s}\)
- 代入初始条件:\(sX(s) – 2 = 3X(s) + \frac{6}{s}\),整理得 \(X(s) = \frac{2s + 6}{s(s – 3)}\)
- 部分分式分解:\(X(s) = -\frac{2}{s} + \frac{4}{s – 3}\)
- 逆变换:\(x(t) = -2 + 4e^{3t}\)
3. 二阶 ODE 示例(Second-Order ODE Example)
求解:\(\frac{d^2x}{dt^2} + x = \cos2t\),\(x(0) = 0\),\(x'(0) = 1\)
- 变换:\(s^2X(s) – sx(0) – x'(0) + X(s) = \frac{s}{s^2 + 4}\)
- 代入初始条件:\(s^2X(s) – 1 + X(s) = \frac{s}{s^2 + 4}\),整理得 \(X(s) = \frac{s^2 + s + 4}{(s^2 + 4)(s^2 + 1)}\)
- 部分分式分解:\(X(s) = -\frac{1}{3} \cdot \frac{s}{s^2 + 4} + \frac{1}{3} \cdot \frac{s}{s^2 + 1} + \frac{1}{s^2 + 1}\)
- 逆变换:\(x(t) = \frac{1}{3}\cos t + \sin t – \frac{1}{3}\cos2t\)
六、非考内容简要说明(Non-Examinable Content)
1. 积分的拉普拉斯变换(Transforming Integrals)
\(\mathcal{L}\left\{\int_{0}^{t} f(\tau) d\tau\right\} = \frac{F(s)}{s}\)
- 逆变换:\(\int_{0}^{t} f(\tau) d\tau = \mathcal{L}^{-1}\left\{\frac{F(s)}{s}\right\}\)
2. 传递函数(Transfer Functions)
定义:系统输入(input)\(f(t)\) 与输出(output)\(x(t)\) 的拉普拉斯变换之比,即 \(Q(s) = \frac{X(s)}{F(s)}\)
- 应用:分析线性系统的稳态行为(steady-state behavior),如简谐运动(simple harmonic motion)系统。
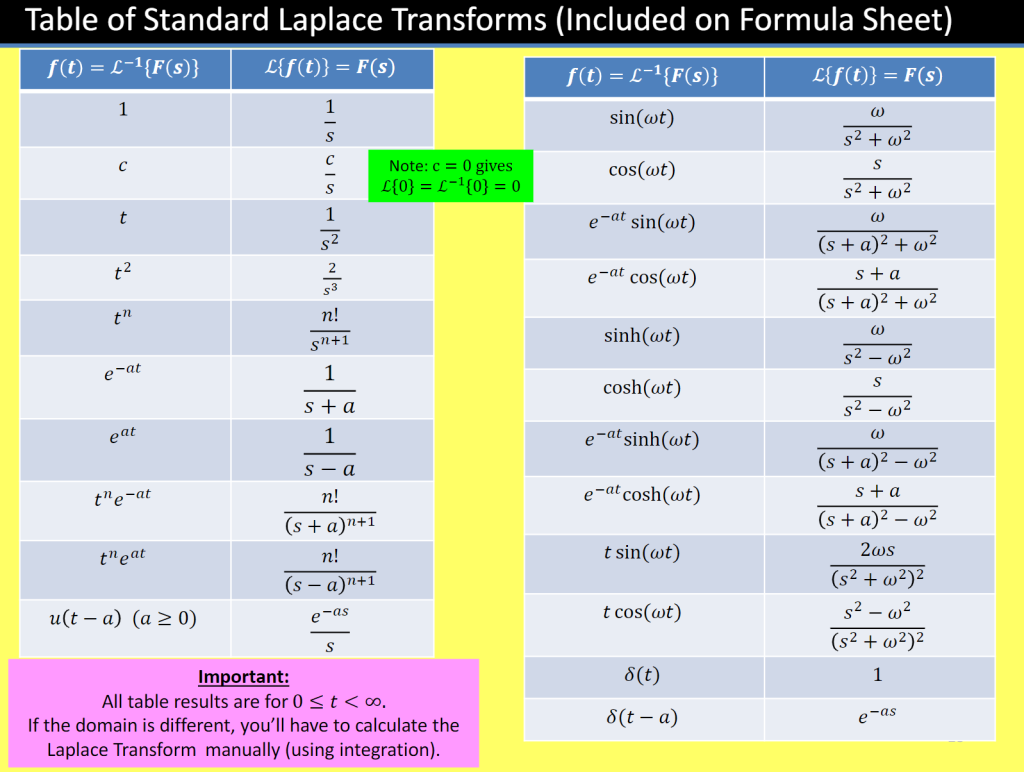
七、考试公式总结表(Exam Formula Sheet)
1. 定义类(Definitions)
| 名称 | 公式 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 拉普拉斯变换 | \(\mathcal{L}\{f(t)\} = F(s) = \int_{0}^{\infty} e^{-st} f(t) dt\) | \(s = \sigma + i\omega\) |
| 逆拉普拉斯变换 | \(\mathcal{L}^{-1}\{F(s)\} = f(t)\) | 查表 + 部分分式 |
2. 基本变换(Basic Transforms)
| 时域函数 \(f(t)\) | 拉普拉斯变换 \(F(s)\) | 收敛条件 |
|---|---|---|
| 1(常数函数) | \(\frac{1}{s}\) | \(s > 0\) |
| \(e^{at}\) | \(\frac{1}{s – a}\) | \(s > a\) |
| \(e^{-at}\) | \(\frac{1}{s + a}\) | \(s > -a\) |
| \(t^n\)(n 为非负整数) | \(\frac{n!}{s^{n+1}}\) | \(s > 0\) |
| \(\sin\omega t\) | \(\frac{\omega}{s^2 + \omega^2}\) | \(s > 0\) |
| \(\cos\omega t\) | \(\frac{s}{s^2 + \omega^2}\) | \(s > 0\) |
| \(\sinh\omega t\) | \(\frac{\omega}{s^2 – \omega^2}\) | \(s > |\omega|\) |
| \(\cosh\omega t\) | \(\frac{s}{s^2 – \omega^2}\) | \(s > |\omega|\) |
| \(u(t – a)\)(单位阶跃函数) | \(\frac{e^{-as}}{s}\) | \(s > 0\),\(a \geq 0\) |
3. 核心性质(Key Properties)
| 性质 | 公式 |
|---|---|
| 线性性质 | \(\mathcal{L}\{af(t) + bg(t)\} = aF(s) + bG(s)\) |
| 频域平移 | \(\mathcal{L}\{e^{-at}f(t)\} = F(s + a)\) |
| 时域平移 | \(\mathcal{L}\{f(t – a)u(t – a)\} = e^{-as}F(s)\) |
4. 导数变换(Derivative Transforms)
| 导数阶数 | 公式 |
|---|---|
| 一阶导数 | \(\mathcal{L}\left\{\frac{df}{dt}\right\} = sF(s) – f(0)\) |
| 二阶导数 | \(\mathcal{L}\left\{\frac{d^2f}{dt^2}\right\} = s^2F(s) – sf(0) – f'(0)\) |
| 三阶导数 | \(\mathcal{L}\left\{\frac{d^3f}{dt^3}\right\} = s^3F(s) – s^2f(0) – sf'(0) – f”(0)\) |
5. 积分变换(Integral Transform,非考)
\(\mathcal{L}\left\{\int_{0}^{t} f(\tau) d\tau\right\} = \frac{F(s)}{s}\)
八、考试易错点(Exam Common Mistakes)
- 符号错误(Sign Errors):
- 导数变换中初始条件的符号:二阶导数公式是 \(s^2F(s) – sf(0) – f'(0)\),勿漏负号;
- 频域平移定理:\(\mathcal{L}\{e^{-at}f(t)\} = F(s + a)\),不是 \(F(s – a)\)。
- 收敛条件(Convergence Conditions):
- 忘记标注收敛条件(如 \(s > 0\)),虽不影响计算,但考试可能扣分;
- 忽略 \(e^{-st} \to 0\)(\(t \to \infty\))的前提是 \(s > 0\),否则积分发散(diverge)。
- 部分分式分解错误(Partial Fractions Mistakes):
- 分子次数高于分母时,未先做多项式除法(polynomial division);
- 不可约二次因式分解时,分子误写为常数(应为一次多项式 \(As + B\))。
- 书写混淆(Notation Confusion):
- 字母 s(complex variable)与数字 5 书写区分,避免阅卷误判;
- 时域函数(小写 \(f(t)\))与频域函数(大写 \(F(s)\))大小写混淆。
- 初始条件代入(Initial Conditions Substitution):
- 解 ODE 时,忘记代入初始条件直接求逆变换,导致结果错误;
- 初始条件为非零值时,计算代数方程时出错(建议分步整理)。
- 线性性质误用(Linearity Misuse):
- 误认为 \(\mathcal{L}\{f(t)g(t)\} = F(s)G(s)\)(错误!拉普拉斯变换不满足乘积性质)。
0 条评论