Summary
| Physical Quantity | First-order Transformation | Second-order Transformation | Key Note (重点) |
|---|---|---|---|
| $G$ | Continuous | Continuous | Equilibrium requires equal $G$ for both phases. |
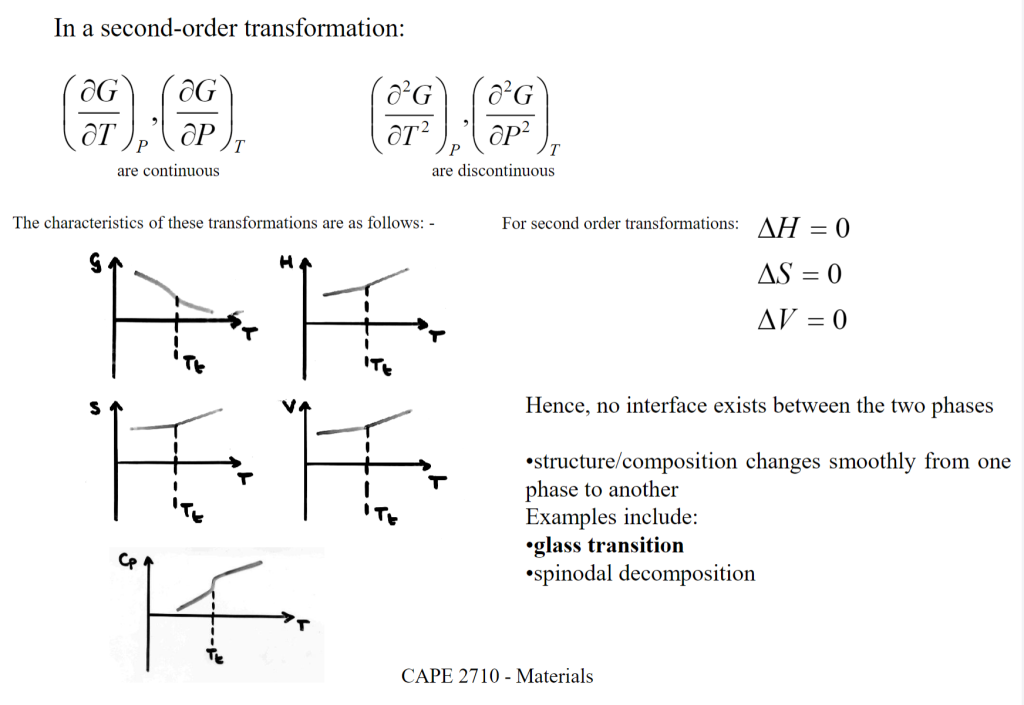
| $S, V, H$ | Discontinuous | Continuous | First-order has latent heat/volume change; second-order does not. |
| 1st derivatives of $G$ | Discontinuous | Continuous | Tied to $S$ and $V$ continuity. |
| 2nd derivatives of $G$ | Continuous | Discontinuous | Second-order has sudden heat capacity change. |
| Interface | Exists (clear boundary) | None (smooth transition) | First-order needs “nucleation + growth” to form new phase . |
| Latent Heat | Yes | No | – |
The core function is:
$$G=H-TS$$
Where:
- $G$ = Gibbs free energy
- $H$ = Enthalpy (related to energy of bonding)
- $S$ = Entropy (related to atomic order)
- $T$ = Temperature
First-order的$H,S$不连续,因此具有明显的interface;而Second-order的$H,S$是连续点,不具有鲜明的interface,因此二阶相变不涉及interface energy.
First-order transmission的interface energy(surface energy)是 “nucleation” 的阻力 —— 需要过冷度提供额外能量来克服界面能,才能形成新相的晶核.
Second-order transition
0 条评论