Crystal Symmetry Elements
$$\text{Fold Number}=\frac{360^{\circ}}{\text{Smallest Rotation Angle that makes the object look identical}}$$
不存在5-fold和高于6-fold的旋转轴:

以上是lecture1的内容,以下是lecture2:
Lattice
$$\text{LATTICE}+\text{MOTIF}=\text{CRYSTAL}$$
Rules for Choosing a Unit Cell
In crystallography, we pick a unit cell by following two rules (in order):
- It must have the same symmetry as the whole crystal structure.
- Example: If a crystal is cubic (symmetric like a cube), its unit cell must also be cubic.
- It must contain the smallest number of lattice points.
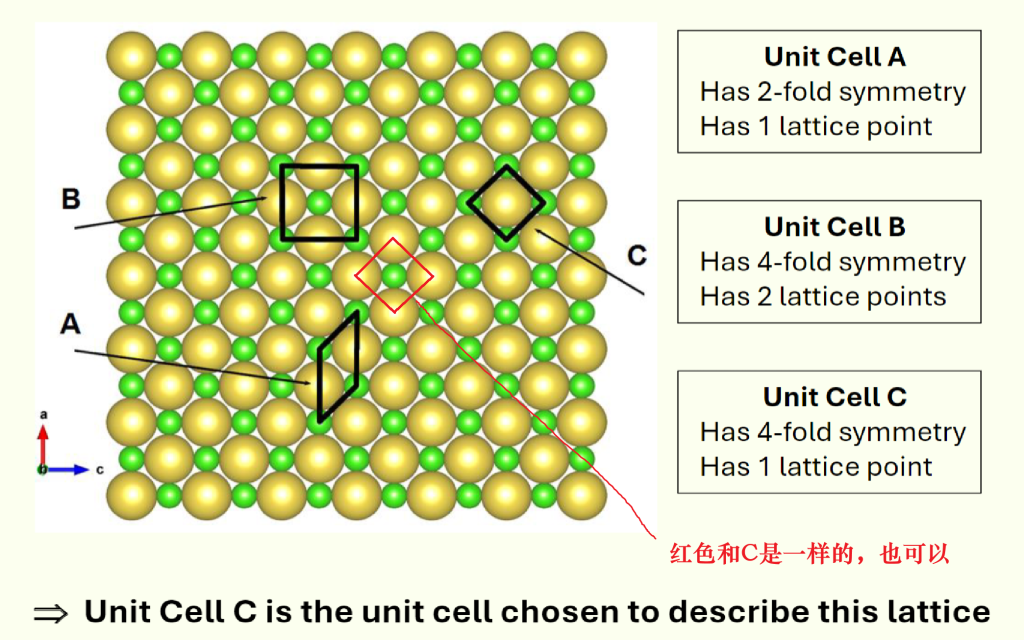
Tips
- The crystal’s symmetry is determined by the whole atom pattern, not by the unit cell
- Higher fold symmetry is better
Primitive Unit Cell
我还是没完全理解这个概念,仅仅有一个点不是无敌了吗,无论要形成什么晶体都可以
Directions and Lines (2D)
2D晶格类型
共有5种,每种的关键区别在于边长关系|a|和|b|的夹角φ
1.Oblique lattice:|a|≠|b|,φ≠90°;对称性最低
2.Rectangular lattice:|a|≠|b|,φ=90°;具有矩形对称性
3.Centered Rectangular lattice:|a|≠|b|,φ=90°;在矩形晶格的中心额外有 1 个晶格点
4.Squared lattice:|a|=|b|,φ=90°;对称性高,含 4 次旋转轴
5.Hexagonal lattice:|a|=|b|,φ=120°;含 6 次旋转轴,是 2D 密堆积的典型晶格
2D Miller indices
Miller 指数不是 “截距比例”,而是 “单位晶胞内线的密度比例”,体现晶体周期性下”线的密集程度“
1.找截距
找一条不过原点的线,记录它在a轴和b轴的截距
2.转分数截距,截距/晶胞长度
3.取倒数,消去∞
4.简化,乘最小公倍数
0 条评论