DC Electric current and circuits
基本概念
Electrical potential difference – Voltage 电势差 – 电压
Resistivity 电阻率
$$ \rho=\frac{1}{ne\mu_e} $$
- $n$: free electrons per unit volume
- $\mu_e$: electron mobility
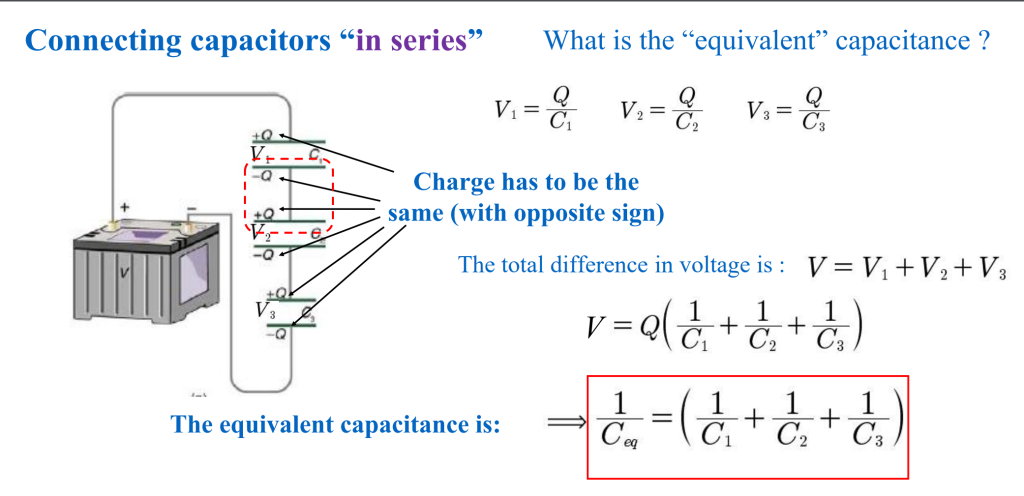
Capacitance
$$ C=\varepsilon\frac{A}{D} $$
其中$\varepsilon=\varepsilon_0\varepsilon_r$
$$ C=\frac{Q}{\Delta V} $$
Units-farad(F)
Mechanical load Torque
$$ \tau_m=k_m\Phi I $$
- $mechanical\ load \approx 0\Rightarrow V_R\approx 0 \Rightarrow \tau\rightarrow0$
- $mechanical\ load \approx \infty \Rightarrow V_R\rightarrow V_s\Rightarrow \tau \rightarrow k_m\Phi \frac{V_s}{R}$
Magnetic moment (magnetic dipole moment)
基本定律
Ohm’s Law
$$ V=IR $$
Kirchhoff‘s rules
- KCL (Junction Rule)
$$ \sum V_{rise} – \sum V_{drop}=0 $$
$$ \Rightarrow \sum_{loop} V_i=0 $$
- KVL:电能守恒
两种电路
Serial resistance

Total EMF: $E^{tot} = E_1+E_2+\cdots$
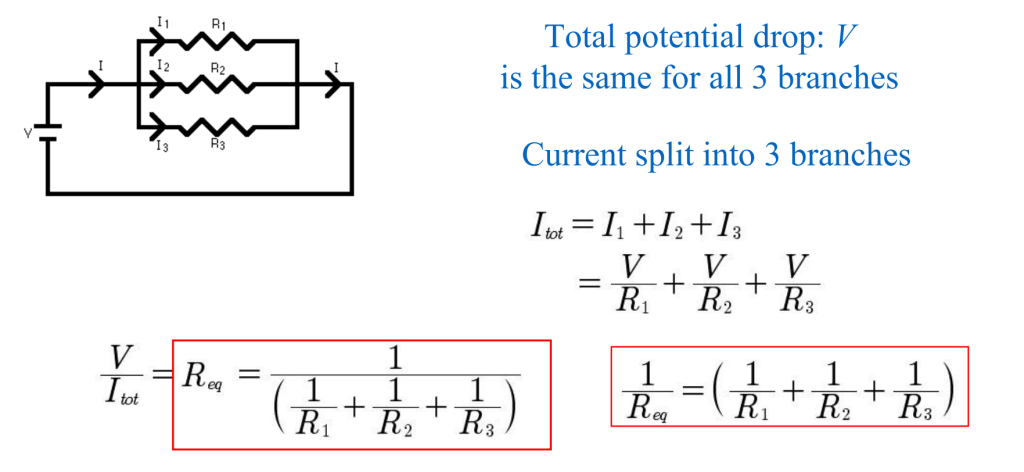
Parallel resistance
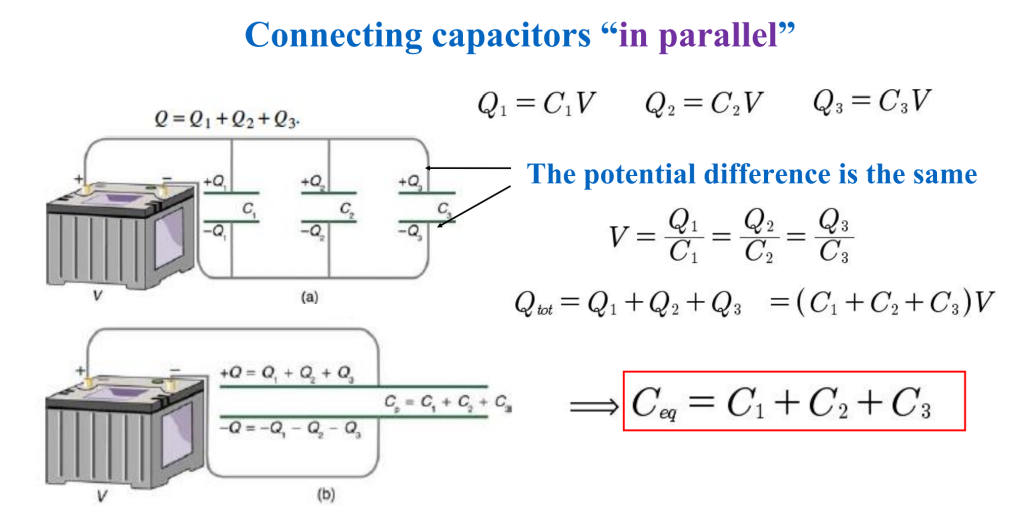
Summary
电流激发磁场的几种情况:
- 通电螺线管
$$B=n\mu_0 I$$ - 通电直导线
$$ B=\frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi L} $$ - 带电圆环
$$ B=\frac{\mu_0 I}{2\pi R}$$ - 带电平行圆盘之间
$$ B=\frac{\mu_0 I_1I_2 A}{2\pi d}$$
基本粒子及射线
粒子
Electron has smaller mass than proton.
electron
- 电量:$-1.6\times10^{-19}C$
- 质量:$9.11\times10^{-31}kg$
射线
x rays
- 粒子:electron
- 频率范围:
Thermodynamics
基本概念
Fahrenheit & Degree Centigrade
$$T_K(K) = T_C(^{\degree}C)+273.15$$
Latent Heat – changing phase
$$Q=mL$$
Where $L$ is the SPECIFIC LATENT HEAT.
$L – (J/kg)$
$m – (kg)$
Heat Capacity
$$ Q=mc\Delta T$$
Where $c$ is the SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY.

Thermal Conductance & Resistance
Heat Capacity
$$C = \lim_{\Delta T\rightarrow0}\frac{\Delta Q}{\Delta T}$$
- At constant pressure
$$C_p=\frac{\delta Q}{dT}$$
Molar Heat Capacity
$$c_m=\frac{C}{n}$$
$$\Rightarrow c_m=\frac{Q}{n\Delta T}$$
Internal energy
For the ideal gases:
$$U=\frac{3}{2}nRT$$
附录
附录2:DC Electric current and circuits
Resistivity
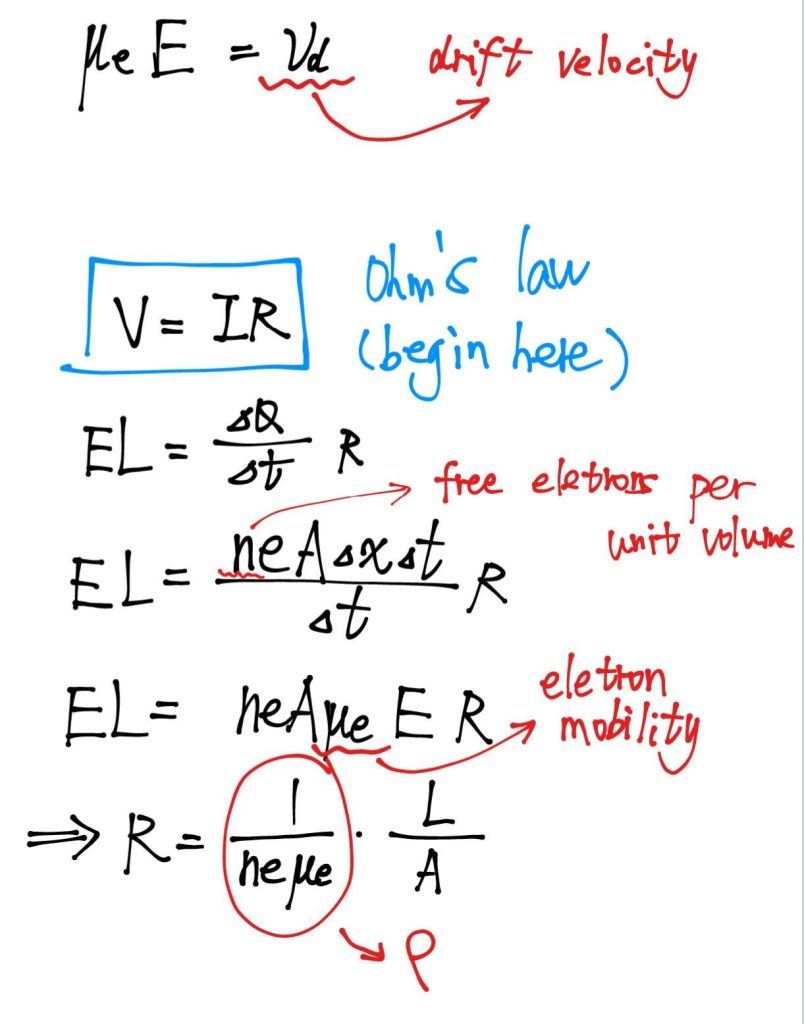
Kirchhoff‘s rules
热力学
0 条评论