在上一篇文章中(Lattice, Basis and Crystal)介绍了晶体的定义。现在是时候更进一步了,我们将讨论晶体结构的可视化和晶体分类的问题。
就像此前提到的,理想晶体是无限的,因此不能用单一图像来表示整个晶体。但是有一点可以加以利用,晶体是由最小元素的构成的,这些元素在各个方向上重复,充满了整个空间.
晶胞 Unit Cell
这些构成晶体的基本单元称为晶胞,满足以下条件:
- 重复排列可以构建整个晶体,而不会有重叠或间隙
- 不可进一步分割
对于确定的晶体,有不同的晶胞划分方式:

Here are some examples for a two-dimensional lattice.
通常,我们选择对称程度最高的作为晶胞.
原胞 Primitive Cell
原胞是仅包含一个晶格点的晶胞. 是理论上最小的晶胞.
如果一个格点在晶胞边缘,那么它就将被另一个晶胞共享,因此只计为一半. 同理,位于立方晶胞顶点的格点被计为$\frac{1}{8}$.
维格纳-塞茨原胞 Wigner-Seitz Cell
W-S原胞是一种特殊的原胞. 它被定义为空间中与W-S原胞中格点的距离小于与任何其它格点的距离的点的轨迹. 它可以按照下图所示构造:
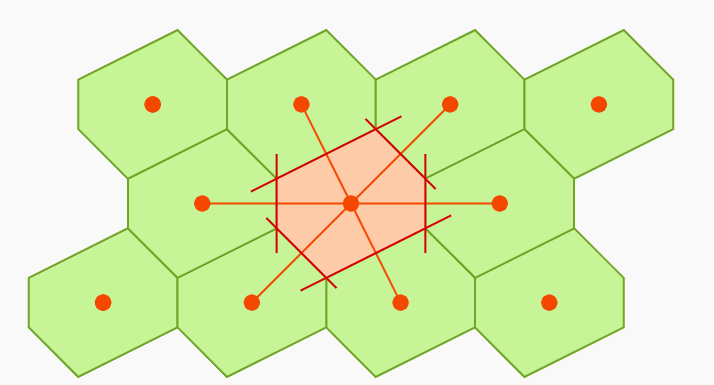
In a second step one constructs the perpendicular bisectors of the connecting lines. The enclosed area is the Wigner-Seitz cell. It forms a unit cell, i.e. is able to build the whole lattice without gaps/overlaps.
Refernce
https://www.physics-in-a-nutshell.com/article/5/unit-cell-primitive-cell-and-wigner-seitz-cell
0 条评论